Introduction to Mirth Connect
As a technology lead at Medisure, I’m currently exploring innovative solutions to modernize our laboratory information systems, with a particular focus on integrating diverse medical equipment with our Laboratory Information System (LIS). Our research is centered on addressing the complex challenge of routing messages from various laboratory instruments, which generate data in HL7 v2.5 format.
Mirth Connect has emerged as a promising solution in our technology research, serving as a powerful, open-source healthcare integration engine designed to facilitate complex message routing and transformation across various healthcare systems. As we evaluate potential middleware solutions, Mirth Connect stands out for its ability to enable communication between different medical software applications, medical devices, and information systems.
At Medisure, our current research with Mirth Connect aims to:
- Investigate methods for receiving HL7 v2.5 messages from various laboratory instruments
- Explore transforming these messages into a format compatible with our REST API
- Develop strategies for routing processed data to our Laboratory Information System
- Assess robust error handling and logging mechanisms
At its core, Mirth Connect presents itself as a potential middleware solution that can:
- Receive messages from multiple sources (HL7, MLLP, DICOM, etc.)
- Transform and route messages between different systems
- Support various communication protocols
- Provide robust logging and error handling
- Offer extensive customization through JavaScript-based channel configurations
Scenario: MLLP Message Routing to LIS via REST API
In this post, we’ll walk through a proof-of-concept for setting up a Mirth Connect channel that:
- Listens for incoming MLLP (Medical Laboratory Lightweight Protocol) messages
- Processes and transforms these messages
- Submits the processed data to a Laboratory Information System (LIS) using a REST API
Prerequisites
- Mirth Connect installed
- Access to a Laboratory Information System with a REST API
- Basic understanding of HL7 message structure
- JavaScript knowledge for message transformation
Step 1: Create a New Channel in Mirth Connect

- Open Mirth Connect Administrator
- Navigate to Channels > New Channel
- Set the following basic channel properties:
- Name: “MLLP to LIS Router”
- Description: “Channel for routing MLLP messages to LIS REST API”
Step 2: Set Data Types
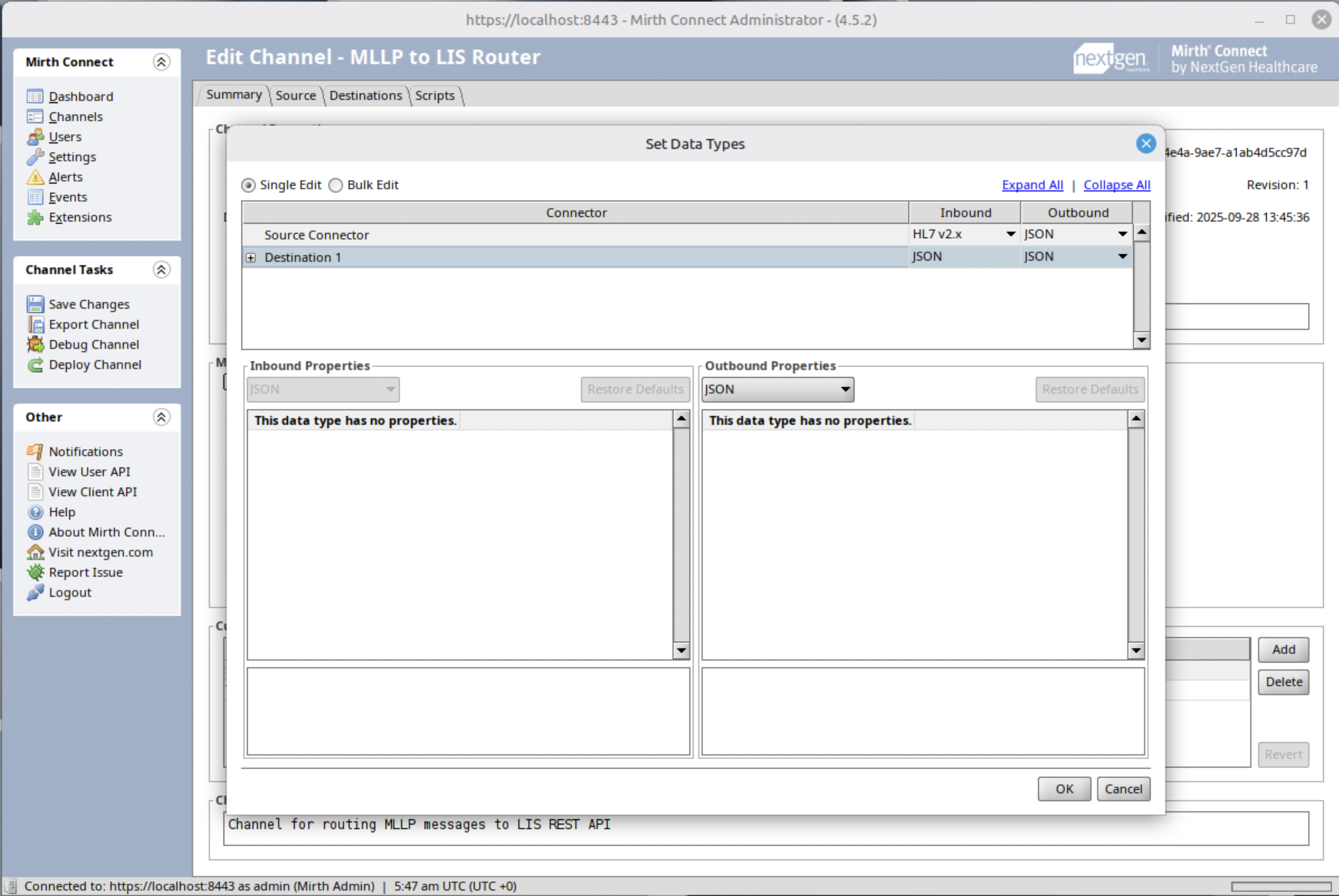
- Set the Outbound of the source connector to JSON.
- Do the same for the destination connector.
Step 3: Configure Source Connector
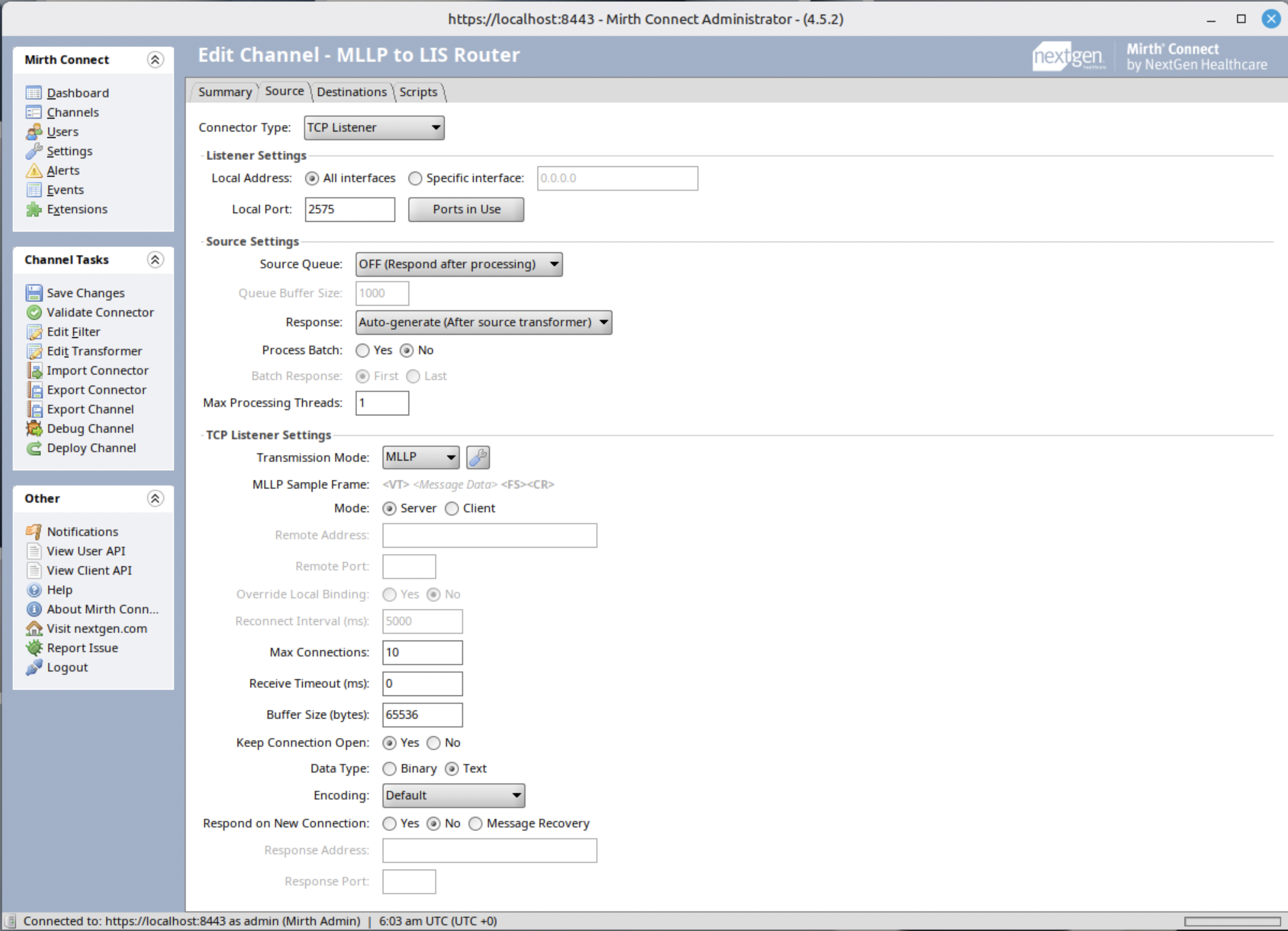
- Connector Type: TCP Listener
- Set the listening port (e.g., 2575)
- Transmission Mode: MLLP
Step 4: Message Transformation
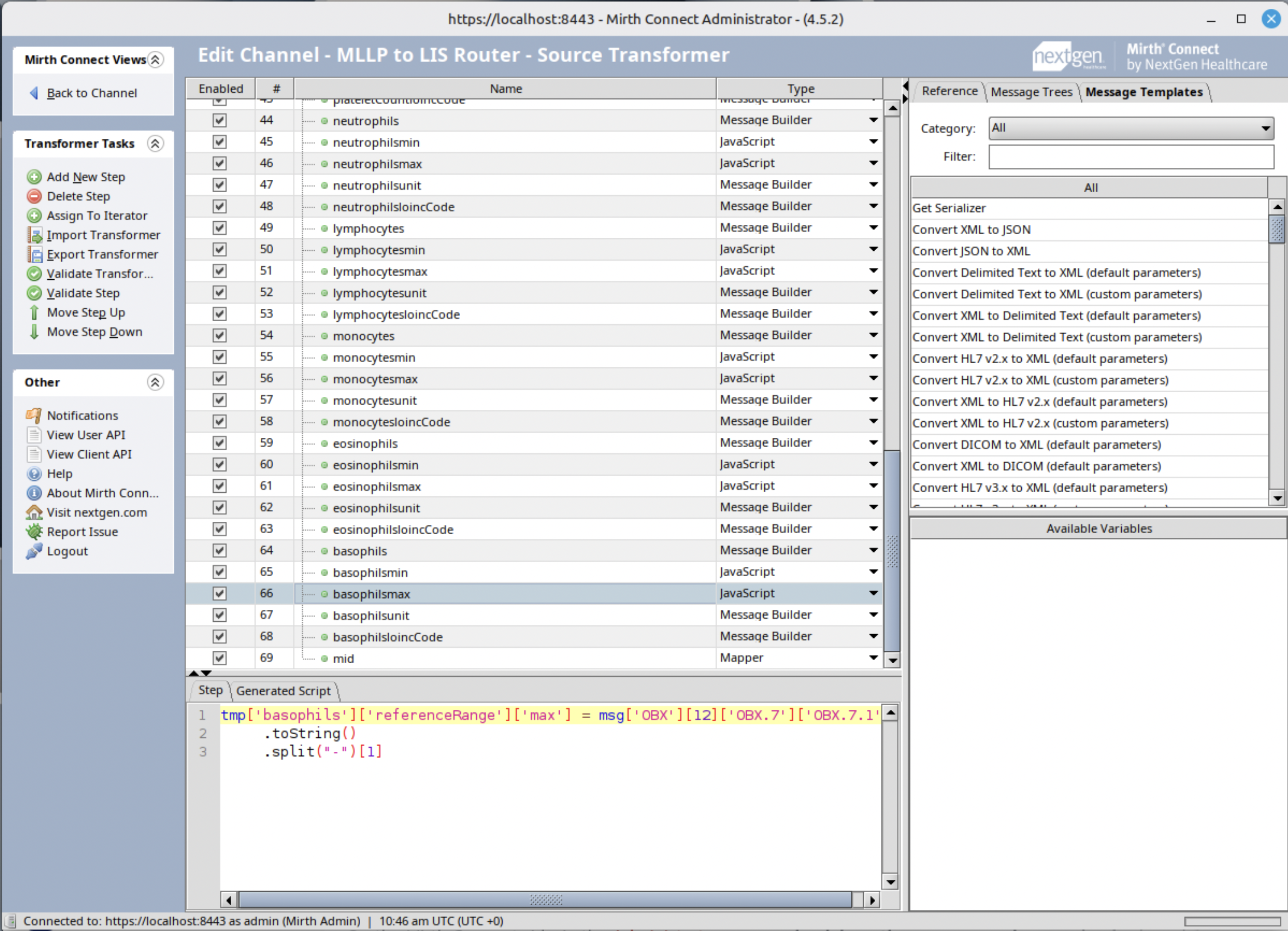
Create transformers to convert the MLLP message. The following is an example of a JavaScript transformer for setting basophils reference max range.
tmp['basophils']['referenceRange']['max'] = msg['OBX'][12]['OBX.7']['OBX.7.1']
.toString()
.split('-')[1]
Step 5: Configure Destination Connector (File Writer)
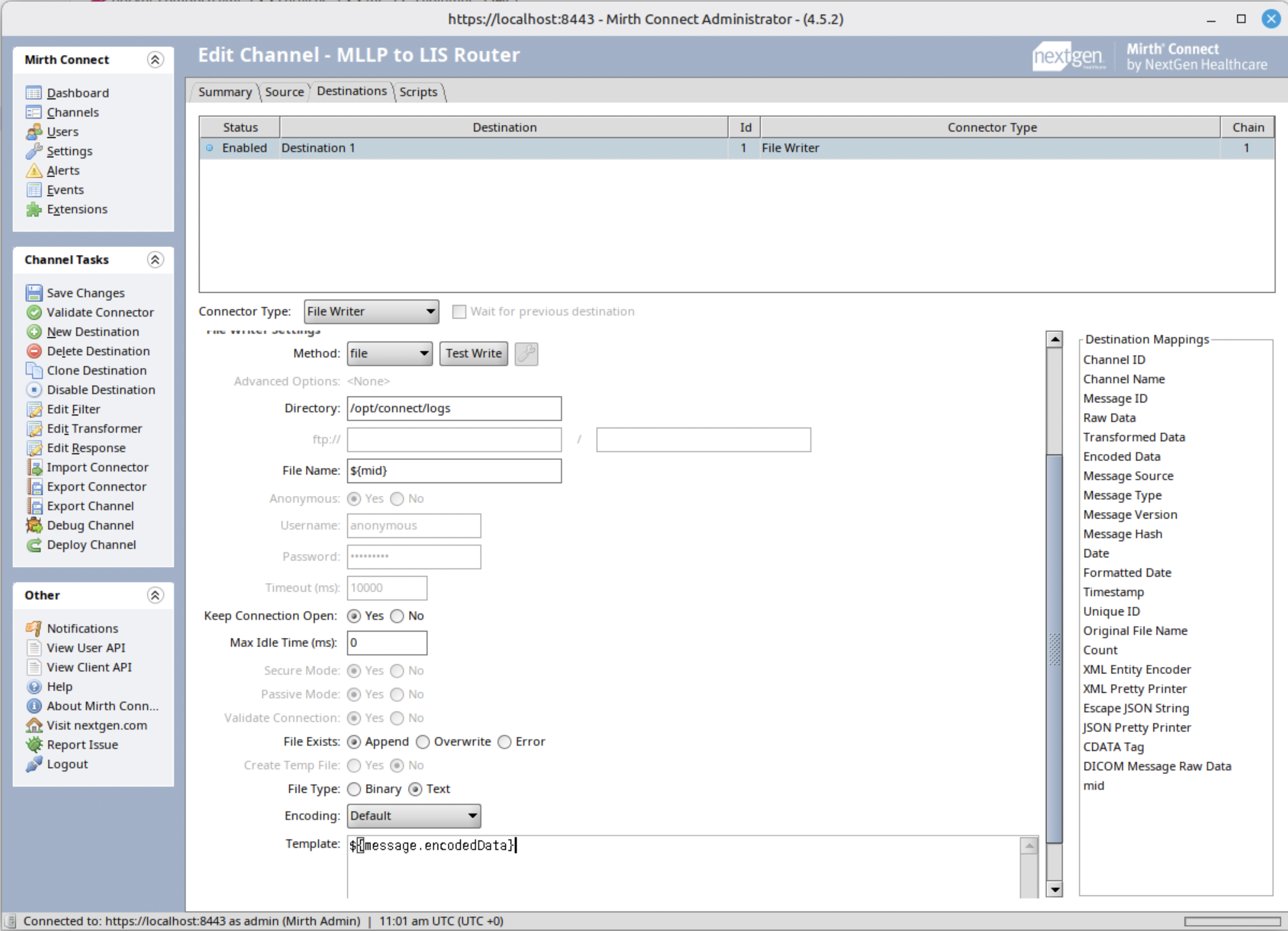
To test out, let’s create a file writer to check if we can successfully parse the HL7 data into JSON.
- Set the directory Mirth connect can write and you have access to.
- Click and drag the mid mapping to use it as the filename.
Step 6: Send a test message
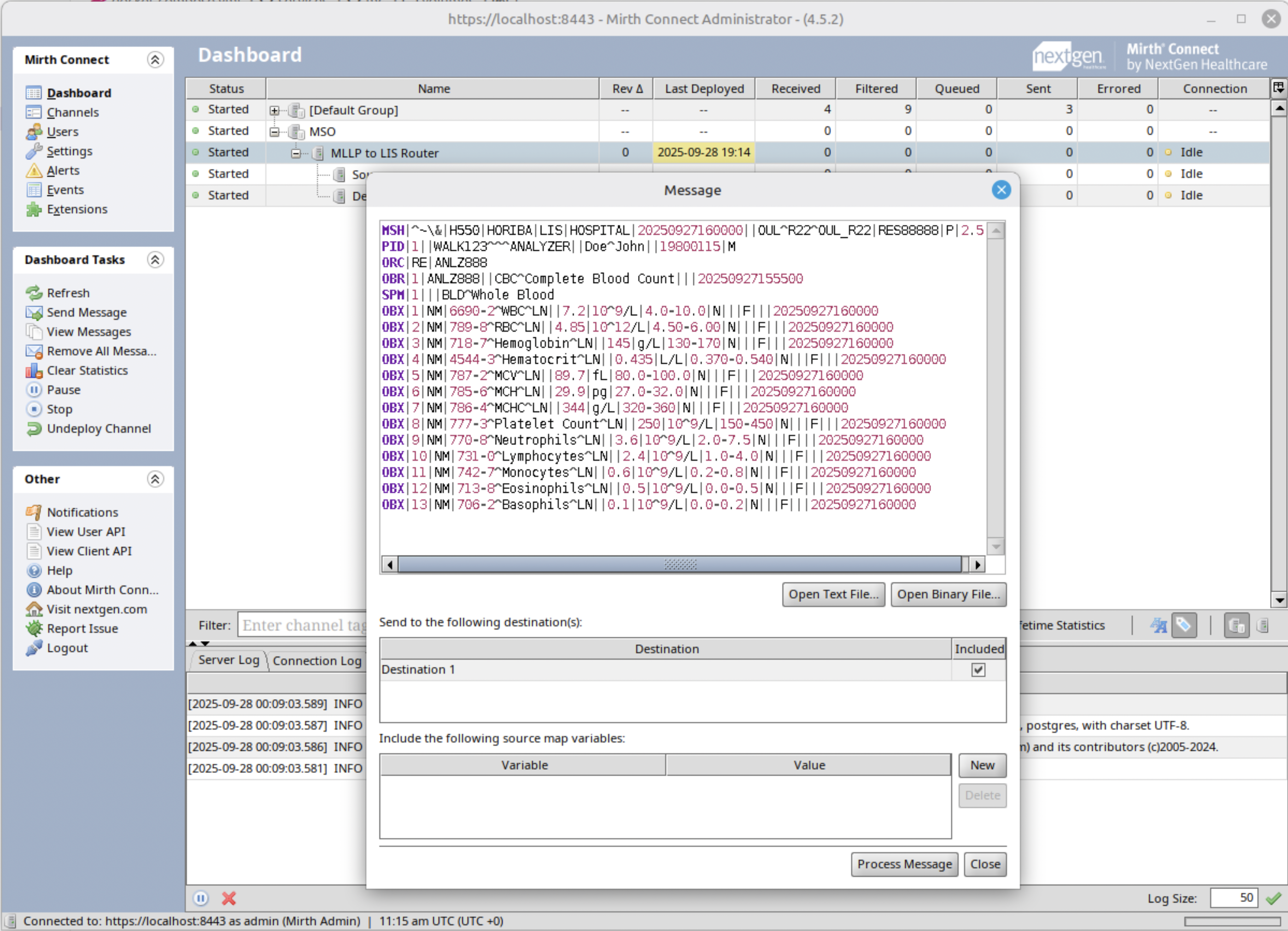
Send a test message and check if the generated JSON file is valid. It should look like this.
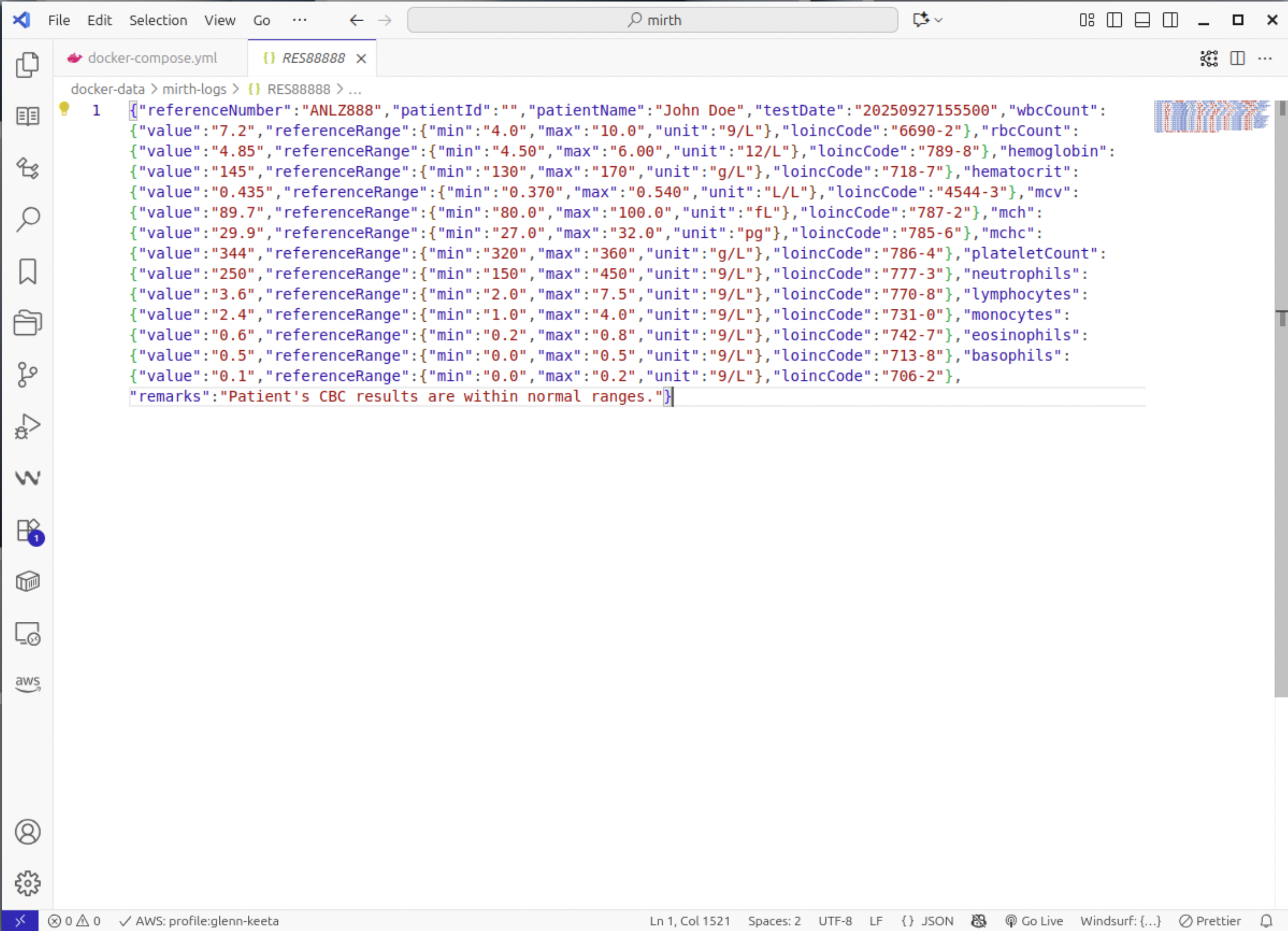
Step 7: Configure Destination Connector (REST API)
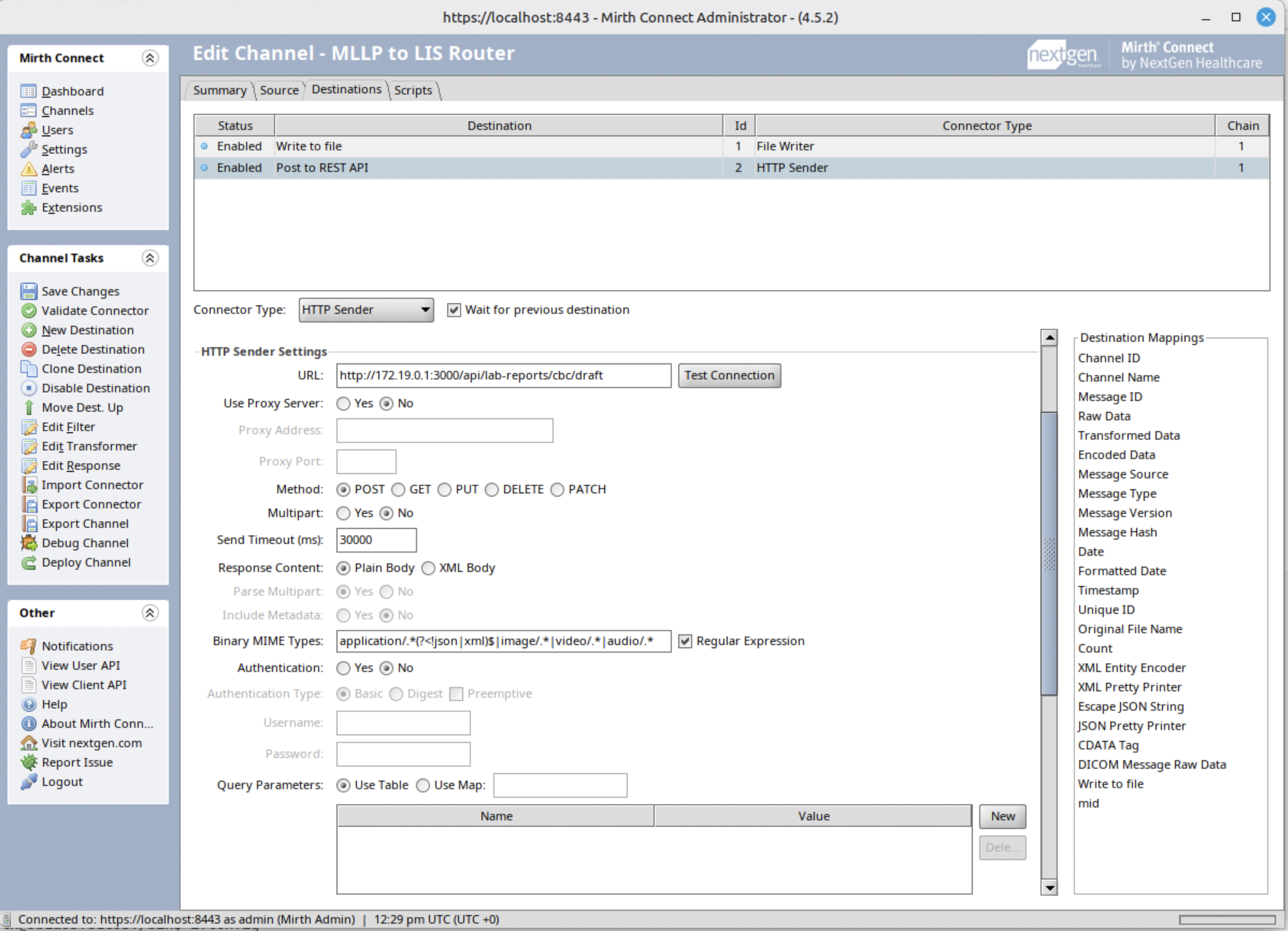
- Set the LIS REST API endpoint URL
- Configure HTTP method (typically POST)
- Set content type to application/json
- Add necessary authentication headers
Step 8: REST API Validation Failure Test
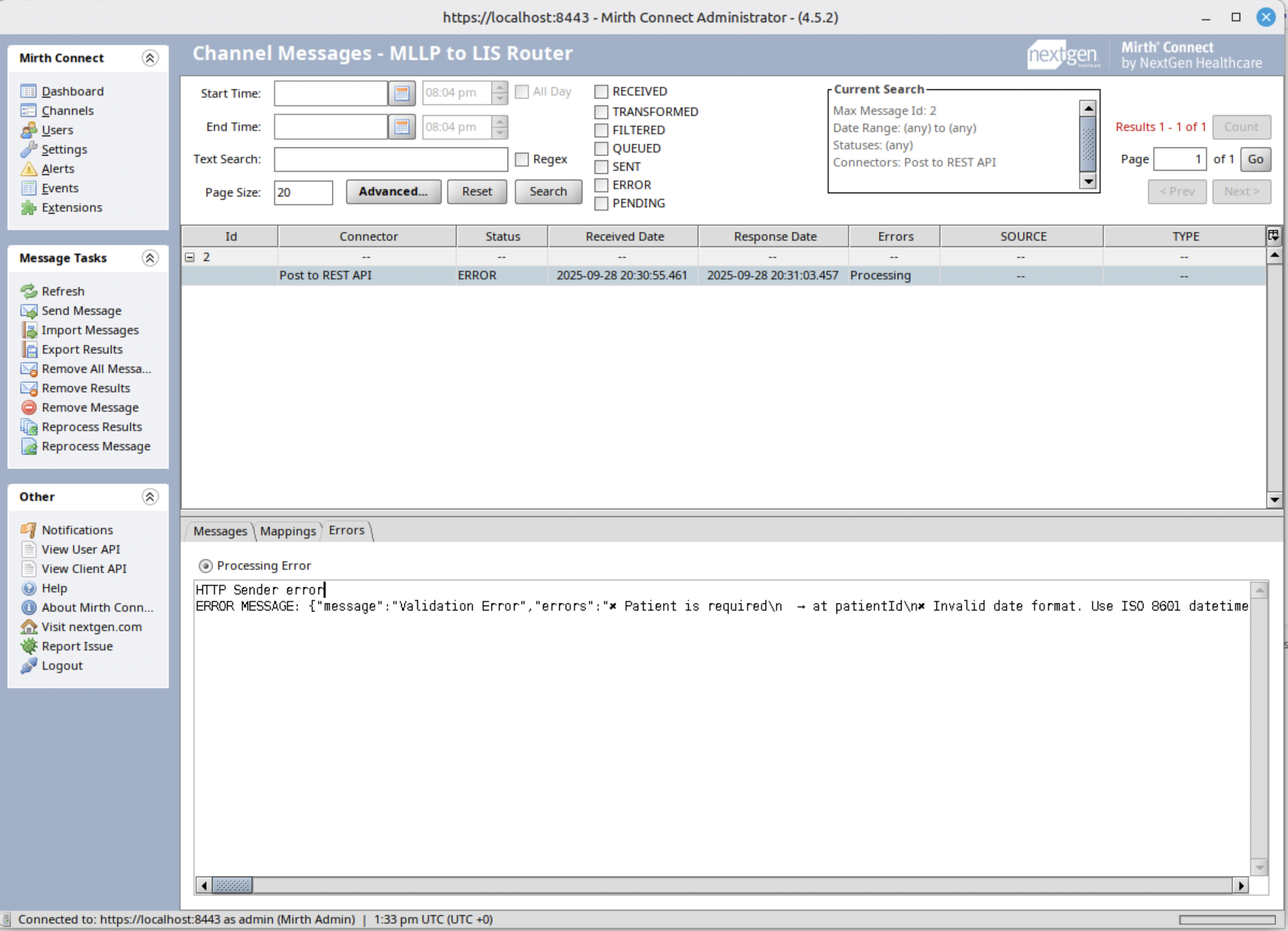
During our testing phase, we encountered an interesting scenario that highlights both the capabilities and challenges of healthcare integration systems. Our Mirth Connect channel successfully demonstrated its ability to submit data to the Laboratory Information System’s REST API, while also revealing important insights into data validation complexities.
The test run showed that while Mirth Connect could successfully route the transformed MLLP message to the REST API endpoint, the message encountered validation failures. Specifically, the test revealed that:
- Some required fields were missing or improperly formatted
- Data type mismatches existed between the transformed HL7 message and the REST API’s expected schema
- Certain validation rules, such as range checks or enumeration constraints, were not satisfied
Despite these validation challenges, this test was a significant milestone. It proved that:
- Mirth Connect can effectively transform MLLP messages into a format suitable for REST API submission
- The integration middleware successfully established communication with the LIS REST endpoint
- We have a clear path for refining message validation and transformation
This test underscores the critical need for:
- Comprehensive message validation in Mirth Connect
- Detailed error logging
- Potential pre-processing of messages to ensure compliance with REST API requirements
Best Practices
- Implement message queuing for resilience
- Implement comprehensive logging
- Regularly monitor channel performance
- Set up alerts for processing failures
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can create a robust Mirth Connect channel that seamlessly routes MLLP messages to a Laboratory Information System via REST API, enhancing interoperability and data flow in healthcare environments.